|
| |
 |
Urine Specimen Validity (Adulteration)Test (S.V.T.)
Six parameter,
one-step professional sample adulteration and contamination test
(Dip Stick Reagent Type)

|
The One Step S.V.T.
urine adulterant test strip is a semi-quantitative, color comparison
screen for the detection of creatinine, nitrite, glutaraldehyde, pH, specific
gravity, and oxidants/pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) in human urine. The test
is intended as a point of testing adulterant pre-screen test of urine samples
prior to further testing. The One Step S.V.T. test will detect for all the
commonly used methods of sample manipulation and adulteration including
dilution, substitution, chemical additives and the so called commercially
available "cleansing agents". |
|
Principle:
Urine sample adulteration is serious problem in forensic
urine drug testing. Sample adulteration is usually achieved by substitution,
dilution or the addition of adulterants including so called
"masking agents" sold commercially.
Adulteration is defined as the tampering or
manipulation of a urine specimen with the intention of altering the test
results. The use of adulterants can cause false negative results in drug tests
by either interfering with the screening test and/or destroying the drugs
present in the urine. Dilution may also be employed in an attempt to produce
false negative drug test results. Clinically, the accepted method to test for
adulteration or dilution is to determine certain urinary characteristics such as
creatinine, pH, and specific gravity and to detect the presence of
glutaraldehyde, nitrite and oxidants /pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) in urine.
INTENDED USE:
The One Step S.V.T. strip is a semi
quantitative, color comparison screen for the detection of creatinine, nitrite,
glutaraldehyde, pH, specific gravity, and oxidants/pyridinium chlorochromate
(PCC) in human urine. The test is intended as a point of testing adulterant
pre-screen test of urine samples prior to further testing. The One Step S.V.T.
test will detect for all the commonly used methods of sample manipulation and
adulteration including dilution, substitution, chemical additives and the so
called commercially available "cleansing agents". Each of the
plastic strips contains six (6) chemically treated reagent pads. One (1) minute
following the activation of the reagent pads by the urine sample, the colors
that appear on the pads can be compared with the printed color chart on the
canister. The color comparison provides a semi quantitative screen for
creatinine, nitrite, glutaraldehyde, pH, specific gravity, and
oxidants/pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) in human urine which can help assess
the integrity of the urine sample prior to further testing.
PARAMETERS TESTED:
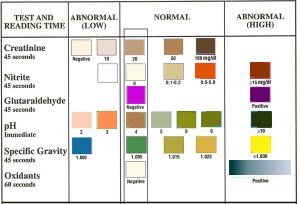 Creatinine is a waste
product of creatine; an amino acid contained in muscle tissue and found in
urine. A person may attempt to foil a drug test by drinking excessive amounts of
water or diuretics such as herbal teas to "flush" the system. Creatinine and
specific gravity are two ways to check for dilution and flushing, which are the
most common mechanisms used in an attempt to circumvent drug testing. Low
creatinine and specific gravity levels may indicate diluted urine. The absence
of creatinine (<5mg/dl) is indicative of a specimen not consistent with human
urine. Creatinine is a waste
product of creatine; an amino acid contained in muscle tissue and found in
urine. A person may attempt to foil a drug test by drinking excessive amounts of
water or diuretics such as herbal teas to "flush" the system. Creatinine and
specific gravity are two ways to check for dilution and flushing, which are the
most common mechanisms used in an attempt to circumvent drug testing. Low
creatinine and specific gravity levels may indicate diluted urine. The absence
of creatinine (<5mg/dl) is indicative of a specimen not consistent with human
urine.
Specific gravity tests for sample dilution. The normal range for specific
gravity is from 1.003 to 1.030. Values outside this range generally indicate
specimen dilution or adulteration.
Nitrite tests for commonly used commercial adulterants such as "Klear" or
"Whizzies". They work by oxidizing the major cannabinoid (marijuana) metabolite
THC COOH˛. Normal urine should contain no trace of nitrites. Positive results
generally indicate the presence of an adulterant.
Glutaraldehyde tests for the presence of an aldehyde. Adulterants such as
"UrinAid" and "Clear Choice" contain glutaraldehyde which may cause false
negative screening results by disrupting the enzyme used in some immunoassay
tests. Glutaraldehyde is not normally found in human urine; therefore, detection
of glutaraldehyde in a urine specimen is generally an indicator of adulteration.
pH tests for the presence of acidic or alkaline adulterants in urine.
Normal pH levels should be in the range of 4.0 to 9.0. Values outside of this
range may indicate the sample has been altered.
Oxidants/PCC (Pyridinium Chlorochromate) tests for the presence of
oxidizing agents such as bleach and hydrogen peroxide. Pyridinium chlorochromate
(sold under the brand name "UrineLuck") is a commonly used adulterant. Normal
human urine should not contain oxidants or PCC.
Test
Procedure
 The
test is based on the color derived from the chemical reaction between the
chemical reagent on each test pad and the urine sample. A color chart
(shown above) indicating
abnormal and normal test result color values for each of the six parameters
tested is printed on the test container. One test strip is dipped in the urine
sample for 1-2 seconds immersing all reagent test pads. The strip is then
blotted on its side to remove excess sample. After one (1) minute the colors of
the six reagent pads are visually compared to the color chart and results
obtained for each of the six test parameters. An abnormal result for any of the
six parameters suggests the sample has been manipulated, altered or otherwise
contaminated and a new sample should be obtained for further testing. The
test is based on the color derived from the chemical reaction between the
chemical reagent on each test pad and the urine sample. A color chart
(shown above) indicating
abnormal and normal test result color values for each of the six parameters
tested is printed on the test container. One test strip is dipped in the urine
sample for 1-2 seconds immersing all reagent test pads. The strip is then
blotted on its side to remove excess sample. After one (1) minute the colors of
the six reagent pads are visually compared to the color chart and results
obtained for each of the six test parameters. An abnormal result for any of the
six parameters suggests the sample has been manipulated, altered or otherwise
contaminated and a new sample should be obtained for further testing.
Availability:
The One Step Urine Specimen Validity Test for
adulterants in urine samples is available in sealed vials containing 25 test
strips. Each vial includes complete testing instructions, technical details and
background information on the test procedure. Volume sales units are indicated
in the table below.
|
Description
|
Packaging |
Sale Unit |
Cost
|
|
|
Urine Specimen Validity
&
Adulteration Test Strip
|
Vial of 25 tests
|
One (1) vial |
$29.50
|
 |
|
|
|
Three (3) Vials |
$80.00
|
 |
|
|
|
Six (6) Vials |
$145.00
|
 |
|
|
|
Twelve (12) Vials
|
$250.00 |
 |
|
|
|
Twenty Four (24)
Vials |
$450.00 |
 |
|
*If the order buttons
are absent or inoperable, please use the pricing
overview page. |
|