|
| |

History of Method Development

Researchers have been observing and studying the phenomenon of ferning in
cervical fluid since 1945, when Papanicolau observed microscopic crystal
formations in cervical fluid (cervical mucus). Subsequent researchers have
studied the ferning of other body fluids, including saliva.
In 1969, Dr. Biel Cassals, a Spanish gynecologist, studied the crystallization
of saliva. His presentation, to the Barcelona Medical Board was in regard to the
relationship between hormonal changes during the female menstrual cycle and the
crystallization of saliva, indicating that the ferning saliva is virtually
identical in appearance to the arborization effect of cervical fluid. He put his
findings into use in 1971 when he developed a microscope intended to test for
ferning in saliva. His clinical experiments involved a number of physicians
testing the apparatus for approximately 10 months on a group of 1,000 women.
These women used the saliva test as a method to ascertain when they were
fertile. According to Biel Cassals, this method's success rate was around 96.2%.
A study conducted in 1991 (M. Guida) at the Institute of Gynecology and
Obstetrics Clinic in Napoli, Italy, achieved a positive result in 92% of the
cases studied, matching salivary ferning to the fertile pre-ovulatory and
ovulatory period. Parameters recorded included basal temperature, subjective
sensation of the mucus at the level of the vulva, characteristics of cervical
fluid, abdominal and/or lumbar painfulness, and echographic proof of ovulation.
A further study conducted in 1992 in Milan, Italy (M. Barbato, A. Pandolfi) and
Naples, Italy, (M. Guida) examined the use-effectiveness of salivary ferning as
a diagnostic testing aid to natural family planning. This study used the PG/53
pocket microscope. They concluded that there is a direct correlation between
salivary ferning and the fertile period. Their conclusion clearly stated that
"Salivary Ferning" may be used as a new parameter to aid women to detect the
fertile period in combination with other sympto-thermal methods of ovulation
detection. The ferning event began on average about 7 days before the first day
of basal body temperature rise. In general, salivary ferning was seen to begin 1
to 2 days before the onset of wet cervical fluid.
In 1992, a study involving 300 women from an IVF (in vitro fertilization)
program was created at the 2nd Department of Gynaecology and Obstetrics in Brno,
Czechoslovakia. Patients were instructed in the use of a hand held microscope to
observe salivary ferning. In all of the patients, the cycle was stimulated by
means of clomiphene citrate/CC/ Gravosan Spofa/and hMG/Pergonal Serono/.
Follicular growth was monitored with a 7 MHz US vaginal sound/Kretz/. Serum 17
beta oestradiol and LH levels were evaluated daily by radio-immune methods.
Basal temperature was also recorded daily. This study found a definite
correlation between oestrogen activity and crystallization of saliva, between LH
curve and crystallization of saliva and between follicular growth and
crystallization of saliva. The study classified reliability as "very high
level", and claimed that combining the sympto-thermal method with the microscope
method resulted in a 99% reliability rate.
The following is the detail of the scientific submission and study:
PROGRESS
REPORT
INTERNATIONAL REVIEW OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
A NEW TEST FOR HUMAN FEMALE OVULATION DIAGNOSIS
Abstract
Material and Method Results References Conclusions
REPRINT
Vol: 6 - Nē 1, 1994 Edizioni Universitarie
Romane Saliva Fertility
Tester
G. GALATI*, E.TRAPANI, M.YACOUB,
M.R. TOCCACELI, G.M. GALATI, C. FIORELLI, F.
BANDIERA, A. PAOLILLO
III Clinica Ostetrica e Ginecologica, Universitā degli Studi di
Roma "La Sapienza" (Direttore: Prof. L. Marzetti)
*Professore Associato - Titolare insegnamento di Fisiopatologia della
Riproduzione.

Abstract

The Authors
performed the saliva test on nē328 women using the Saliva Tester. In nē48 cases
the test results revealed a fern-like crystallized structures as illustrated in
"Figure 3"below. In nē20 cases they performed a Transvaginal Ultrasonography
(T.V.U.S.). In nē16 cases (80%) they found an ovarian follicle greater than 2 cm.
Key words:
Fertility tester, saliva, fertile period, Transvaginal Ultrasonography.
To know the days of
their menstrual cycle when fecundation is possible has always been a demand felt by women
and this both in the case when they want to avoid it (1). Many methodologies exist that
enable us to verify or not the presence of a mature ovarian follicle or its happened
explosion. A very simple methodology was reached with observation and testing of the
Saliva Tester; results that may be easily and directly realized by any woman, at any
moment of the day, anywhere. The prospective advantages that descend as to the knowledge
of the useful days for a fecundation are such that they led us to directly and correctly
try this new test.

Material
and Method

It has been considered
the use of a mini-microscope, or "Saliva Microscope", made up of a small
cylindrical body or eyepiece where we note an optical part with an opposite small slide
where a sample of saliva is placed. As soon as the sample of saliva has dried, the small
eyepiece body is put into a cylindrical container, that leads down to a lighting
system. By focusing the lens, a fern-like characteristic crystallization is pointed out,
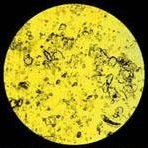
in a very near correlation with the ovulation period (Figure 3). Out of the fertile days
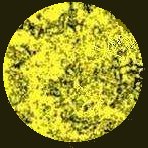
there are no fern-like crystallization structures seen, as pictures named "Figure
1" (during the non-fertile period) and "Figure 2" (during the intermediate
period) indicate.
We have taken into
consideration 328 women between 15 and 50 years old, not using OCP who were placed under
our observation at the out-patients' departments of the Institute of Obstetrics and
Gynecology of the University "La Sapienza" in Rome. No selective principle has
been adopted. We have only invited the patient to leave a sample of saliva on the slide of
the mini-microscope, and afterwards age, day of the cycle in which the patient was and
length of her cycle were noted. 48 women, whose sample of saliva gave the fern-like
characteristically stratification were invited to undergo an ultrasonography with
transvaginal sound for the control of the ovarium and of the presence or not of the
pertinent follicle. 20 women accepted our request, 28 women kindly refused.
|
Figure 1 (Infertile) |
Figure 2 (Intermediate) |
Figure 3 (Fertile) |
|
 |
 |
 |

Results

Results are reported by Tables
1,2 and 3. In Table 1 we see nē48 women of nē328 who, as far as anamnesis is concerned,
are in the ovulation period; nē40 of these women gave us the picture "Figure 3"
type after test, nē40 gave us the picture "Figure 2" and nē248 the picture
"Figure 1" type (Table 2). At the anamnesis, nē 36 women were in the
intermediate period; in all 36 cases of this group, we have noted a picture "Figure
2" type. At the anamnesis, nē 244 women were in the non-fertile period and we have
noted a picture "Figure 1" type in all the 244 cases. In the Table 3, are
pointed out the nē20 cases who, at the saliva test, showed a picture "Figure 3"
type and have accepted to undergo sonographic control by means of transvaginal sound..
Table 1 -Number of women
undergoing the saliva test, correlated to the supposed fertile or non-fertile period of
the cycle.
Day of the cycle |
Non-fertile
period |
Intermediate period |
Fertile period |
Total |
|
N° of women undergoing test |
244 |
36 |
48 |
328 |
Table 2 -Picture stressed by means of the saliva test.
|
Stressed picture |
Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Total |
|
N° Cases |
248 |
40 |
40 |
328 |
Table 3 -Echographic control of nē 20 women by means of picture Figure 3 type of the saliva test
|
Ovarium Echographic Control |
Follicle Absence |
Follicle < 1 cm |
Follicle > 2 cm |
|
N° cases |
0 |
4 |
16 |
In 16 cases, equal to 80% of the
total, an ovarian follicle has been stressed having dimension over 2 cm, in 4 cases a
follicle having diameter less than 1 cm has been stressed.

References

1) Zondek B.,
Rozin S.: Cervical mucus arborization: its use in determining of corpus luteum function.
Obstet. and Gynec., 3: 463, 1954. 2) Barbato M., Boerci M., et al.: Natural methods for
fertility control. New Trends Gynaec. Obstet., 2: 325, 1986.
3) Calamera J.C., Vilar O., Nicholson R., change in sialic acid concentration in human
saliva during the menstrual cycle. Int.Fertility 1986, 31; s.43-45
4) Folan J., Gosling J.P., Finn M.F., Fottrell P.F.; Solid Phase, Enzimoimmunoassay of
estrone in saliva, Clin.Chem., 1989, 35; s.569-571
5) Mancuso S., Van Look P.F.A.: Natural fertility regulation today. Intern. J. Gynecol.
Obstet., Suppl. I, 1989.

Conclusions

A Saliva
Microscope can
be used to help determine the fertile period:
the fertile cycle will be identified with a continuous use, cycle after cycle.
The Tester can
also allow, by repeating every month the tests, to obtain some significant indications
about the monthly cycle behavior and the hormonal situation of the woman. The
tester can also be used to
help avoid an undesired pregnancy:
the comparison of the figures given in Tables 1 and 2 indicate the following: at the
anamnesis n° 244 women were in the
non-fertile period and we have noted a picture "Figure 1" type. In all 244 cases
at the anamnesis n° 36 women were in the
intermediate period; in all 36 cases of this group, we have noted a picture "Figure
2" type. In both cases we had a perfect coincidence between supposed fertile or
infertile days of the cycle and tests executed with "The Saliva Fertility
Tester". At the anamnesis 48 women were
in the fertile period; in 40 of them we have noted a picture "Figure 3" type.
Such difference is due to the fact that 4 of them had a meal one hour before testing, thus
invalidating the result, and the other 4 may have not correctly performed the test.
Therefore, even if we assume that all these 8 women
were in fact fertile (very unlikely), the final result of such test is that ONLY
8 women out a panel of 328, i.e.
less than 3%, resulted in false negative (in fact
fertile) at the saliva testing. WE CAN CONCLUDE
STATING THE FOLLOWING:
-
"TO
OUR KNOWLEDGE THE SALIVA MICROSCOPE CAN
BE SIGNIFICANTLY HELPFUL IN PROVIDING AN ADDITIONAL AID TO WOMEN WANTING TO
IDENTIFY THEIR LIKELY FERTILE PERIOD DURING THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE.
-
THE
OUTCOME IS THAT ITS ACCURACY, IN DETERMINING FERTILE MOMENTS OF THE MONTHLY CYCLE, IS
CLOSE TO 98%, HIGHER THAN OTHER CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES LIKE CONDOM, SPYRAL, DIAPHRAGM, NOT
TO MENTION BILLINGS AND OGINO-KNAUS METHODS, PLACED AT THE LOWER END OF THIS SCALE.
-
TO
PREVENT A PREGNANCY ONLY THE CONTRACEPTIVE PILL HAS A HIGHER RATE (99%) ; AT THE SAME TIME
EVERYBODY TODAY IS AWARE OF BAD SECONDARY EFFECTS OF THE USE OF THE PILL. THIS TESTER IS
NOT INVASIVE AND THERE IS NO NEED OF REAGENTS OR OTHER EVIDENCE SYSTEM.
-
ANY
WOMAN CAN EASILY DO THE TEST. SHE CAN PERFORM IT ANYTIME AND ANYWHERE."
|